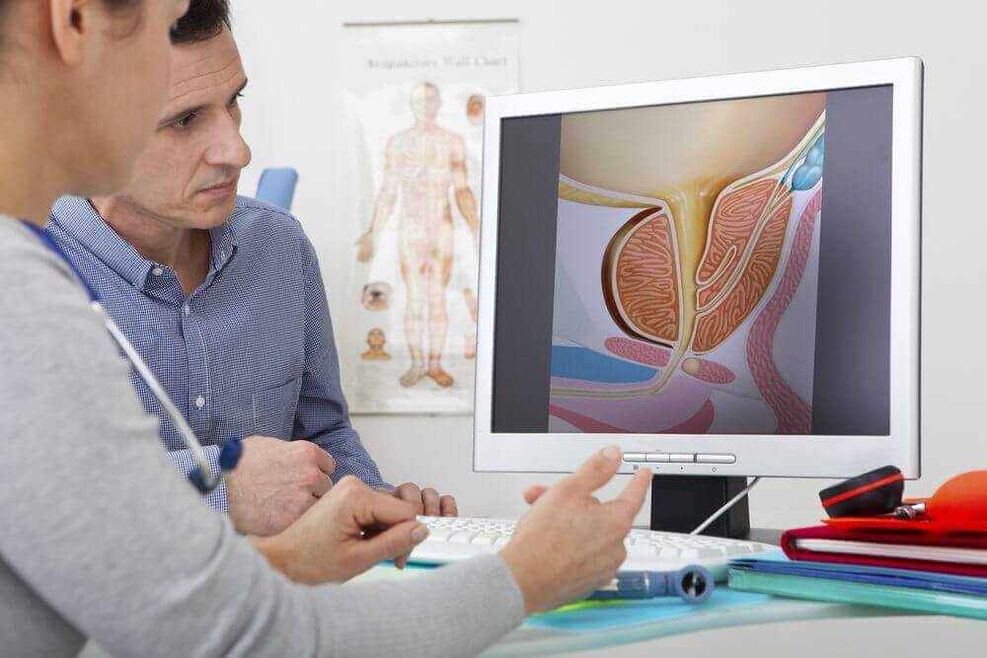
The most common urological pathology for men over 45 to consult a urologist is prostate adenoma. The existence of this pathology greatly impairs the quality of life of men. One of the most terrifying consequences of the pathological process is the degeneration of benign prostatic hyperplasia into a malignant tumor.
To combat prostate adenomas, surgical and medical treatment methods are used. Hospital experts will choose the most effective drug or surgical intervention method according to the stage of the disease, the general condition and age of the patient, and the presence of comorbidities. The surgical clinic creates comfortable conditions for treating patients.
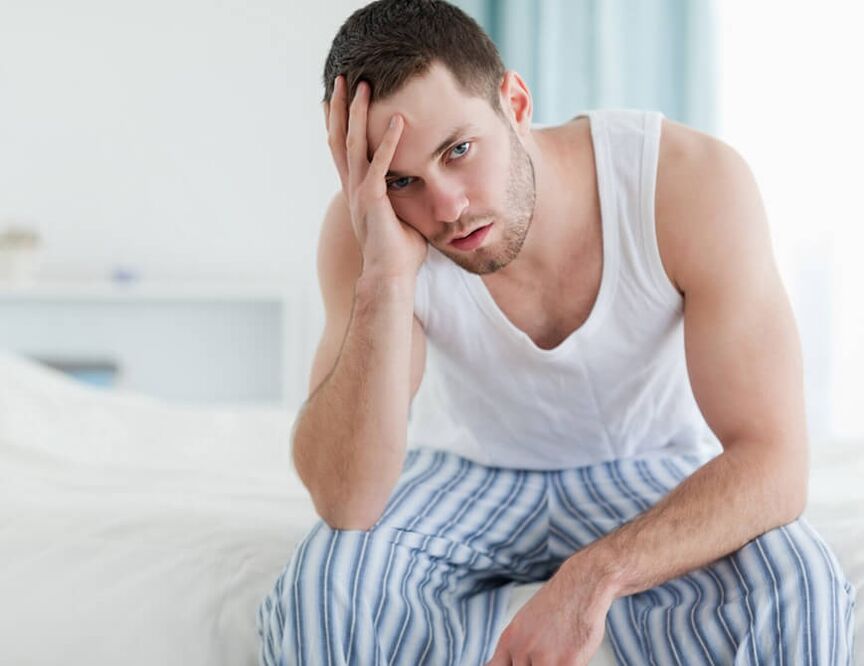

Causes of disease development
The occurrence of adenomas is most often associated with age-related changes in the prostate, that is, changes in its structure and increase in size. As a result of this change, the urethra, which is located in the thickness of the prostate, is gradually compressed and the urination process is disturbed.
Prostatic adenomas in men develop due to hormonal changes in the body caused by age-related changes. The level of testosterone (male hormone) gradually decreases with age, while the concentration of female sex hormone (estrogen) increases instead. This phenomenon is called male menopause.
The development of prostate adenoma may be attributed to the following risk factors:
- Depending on the age of the patient, prostate enlargement is rarely found in men under 40, and prostate enlargement can be diagnosed almost every second after the age of 60.
- Genetic susceptibility-if prostate adenoma is diagnosed in male close relatives, there is a huge risk of inheriting this disease in adulthood;
- Diabetes, cardiovascular disease-benign tumors of the prostate (adenoma) can be caused not only by these diseases themselves, but also by the harmful effects of therapeutic drugs (for example, β-blockers);
- Wrong way of life-obesity, men with insufficient physical activity have an increased risk of prostate adenoma.
symptom
When a person has the following symptoms, a prostate adenoma may be suspected:
- Increased the desire to urinate;
- Appearance of tight abdominal muscles that require urination;
- Pain, burning, poor urine flow;
- Discomfort and insufficient emptying of the bladder;
- Increase the duration of the urination process.
Prostate adenoma not only causes a decline in the quality of life of men, but also causes acute retention of urine in men, which requires surgical treatment. In order to avoid surgery, many patients use special drugs to treat prostate adenomas to eliminate symptoms and restore normal prostate function. However, only qualified experts can recommend the best treatment for prostatitis and prostate adenoma. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to contact him.
The treatment of prostate adenoma is individual for each patient. The attending physician prescribes drugs for the treatment of prostate adenoma, its dosage and duration of use. The treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma alone is not only ineffective, but also dangerous. In view of the existence of certain "personal" chronic diseases among the elderly, comorbidities should be considered and drugs for the treatment of elderly prostate adenomas should be selected.
Stage of disease
Prostate adenoma is characterized by gradual development and can be divided into three stages.
- The first stage of the disease progresses with minimal urinary disturbance. Its frequency may increase slightly, especially at night, and the urine flow is not smooth. The first phase can last from one year to 12 years or more.
- The second stage of prostate adenoma is characterized by more pronounced dysuria: intermittent urine flow, the need to strain during urination, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. Urine remaining in the bladder and urethra can cause inflammation and is accompanied by pain, burning sensation during urination, pain in the waist area and above the pubic bone.
- The third stage is characterized by periodic or continuous involuntary excretion of urine, which forces the patient to use a urine bag.
complication
In some men, prostate adenoma does not worsen the quality of life, and complications do not occur. However, in some cases, the disease may lead to the following negative consequences:
- Acute retention of urine-characterized by sudden inability to empty the bladder and pain in the suprapubic area. In this case, the patient needs emergency medical care through catheterization or minor surgery;
- The occurrence of urinary tract infection-stagnation of urine creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogens, leading to the development of cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- The formation of bladder stones is also the result of stagnant urine.
- Bladder injury-When the bladder empties irregularly, it stretches and forms protrusions (pockets) on the organ wall, where urine stagnates;
- Kidney damage-Increased pressure in the ureter and bladder has a direct damaging effect on the kidneys, leading to renal failure.
Prostate adenoma and potency
Prostate adenoma is closely related to drug efficacy. Adenoma destroys the structure of glandular tissue, which in turn leads to the destruction of another equally important organ, the testicle, which is responsible for the production of androgens. Therefore, prostate adenoma may be the cause of impotence and requires long-term and complex treatment.
Diagnostic procedure
A simple and effective way to establish a preliminary diagnosis is to fix the patient's urination diary through quantitative and qualitative parameters: urination volume, fluid intake, command impulse, and night impulse. The main physical examination method for suspected prostate adenoma is a digital rectal examination of the prostate to detect enlargement and rule out other pathologies.
Use the following laboratory and instrument methods to diagnose prostate adenoma in the hospital:
- Routine blood and urine tests;
- Biochemical blood tests to detect kidney conditions, urea and creatinine levels;
- PSA test (exclude prostate cancer);
- Transrectal ultrasonography (ultrasound);
- Urine flow measurement (to determine the flow rate of urine);
- Determination of residual urine volume (using ultrasound);
- Pelvic floor electromyography;
- Cystoscopy
- Urinary urography.
treatment
The treatment of prostate adenoma is aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the lower urinary tract, improving the patient's quality of life and preventing the development of disease complications. Patients with mild symptoms that do not worsen the quality of life usually receive regular check-ups by urologists and adopt a strategy of regular follow-up. The urologist will monitor the development of the disease and propose how to stop the growth of prostate adenomas. Suggest. During this period, attention is focused on non-drug treatments. The above methods can be used as a supplement to conservative treatment. The following drugs can be taken:
- Alpha blockers (tamsulosin, alfuzosin);
- 5-α reductase inhibitor (finasteride);
- Type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor (sildenafil);
- Combination of 5-alpha reductase inhibitor and alpha receptor blocker;
- Muscarinic receptor blockers or M-anticholinergics.
For patients with advanced prostate adenoma, surgical treatment is recommended, which can be performed by several methods: transurethral resection, transurethral resection and prostate resection.
There are certain indications for the use of surgical treatment:
- Recurrent urine retention;
- Renal failure, caused by prostate adenoma;
- Bladder stones;
- Repeated urinary tract infections;
- Recurrent hematuria.
In addition, in the case of ineffective drug treatment, surgical intervention is necessary for the patient.
During conservative treatment or postoperative period, patients need to undergo continuous medical supervision through standard studies (urinary flow rate measurement, ultrasound, PSA level analysis).
drug
There is a certain plan under which specific drugs for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma are prescribed. Due to the use of α-reductase inhibitors and α-receptor blockers, high therapeutic efficiency can be achieved. These drugs used to treat prostate adenomas in men help eliminate the main symptoms of the disease and restore adequate urination.
What is the most effective and widely used prostate adenoma drug? The list is headed by blockers of α1-adrenergic receptors. In addition, the list also includes 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, vitamins and minerals.
The complexity of drug treatment includes more than just drugs. If it is a prostate adenoma, a bioactive additive-dietary supplement can be added to conservative treatment to enhance the therapeutic effect of the drug and ensure rapid recovery. Some of them contain zinc. This macronutrient is directly involved in spermatogenesis and testosterone synthesis. Phytosterols can normalize urination.
Drug treatment with α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist group
These drugs used to treat prostatitis and prostate adenoma can relax the smooth muscles of the urinary system and improve the flow of urine. Tamsulosin has the same active substance as a part of other drugs (alfuzosin, silodosin, etc. ). It is a highly selective drug that has a positive effect on the prostate muscle and the α1-adrenergic receptor of the prostate. Selectively act on the urethra and bladder. Due to the decrease in muscle tension, the outflow and excretion of urine is promoted. Tamsulosin, like all selective drugs, has minimal side effects and does not affect vascular tone. It can be prescribed to patients with chronic hypertension.
Alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists must be used continuously in order to gradually reduce the irritation and obstruction of prostate adenomas. In the prescriptions of urologists, tamsulosin has a well-deserved priority for the treatment of prostate adenoma.
The tablet form of the drug is considered to be more advanced, because due to the controlled release of tamsulosin, the active substance is present in the body in a constant concentration. The drug enters the bloodstream uniformly, thereby reducing the possibility of the main side effect of the drug in the adrenaline blocker-a sharp drop in blood pressure.
The equivalent drug with the active ingredient tamsulosin is Urorek. Taking the drug will not bring the following adverse effects: orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, and increased frequency of angina pectoris in patients with coronary heart disease, so it can be taken for men with heart disease. Choosing the right dose and following the rules of all drugs that use alpha blockers can achieve good therapeutic effects with almost no side effects.
Reductase inhibitors (blockers) drugs
The drugs in this pharmacology group (finasteride, dutasteride) help to alleviate the outflow of urine, thereby eliminating the main symptoms of the disease. A stable therapeutic effect will be produced within two to three weeks after the start of the treatment. After three months, all symptoms disappeared completely. According to the results of clinical studies, the maximum effect can be obtained after six months of treatment with these drugs.
Finasteride and dutasteride are specific inhibitors of type 2 5-alpha reductase (the cellular enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone). The growth of the prostate in BPH is directly related to this conversion of testosterone. Thanks to the 5-α-reductase inhibitor, the production of dihydrotestosterone in the prostate is blocked and the blood concentration is significantly reduced.
Finasteride and Dutasteride are used for the following purposes:
- Treatment and control of benign prostatic hyperplasia;
- Improve urine outflow and eliminate symptoms of prostate adenoma;
- Reduce the risk of acute urine retention and reduce the need for surgery.
Finasteride and dutasteride have obvious antiandrogenic effects, that is, help reduce the level of male hormones in the blood. In addition, these drugs have teratogenic effects, so they must be used with caution. With the help of modern medicine, it is possible to stop the growth of the prostate and avoid surgical treatment.
Antispasmodics and painkillers can exacerbate the disease
The main purpose of using antispasmodic and analgesic drugs in the progression of prostate adenoma is to relieve the patient's general condition and eliminate pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen) have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. They not only help to resist the pain when urinating, but also help to eliminate persistent pain in the groin and perineum. Due to the effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the inflammatory process is reduced, the swelling of the prostate is reduced, the body temperature is normal, and unpleasant symptoms are eliminated.
Non-opioid analgesics produced in the form of tablets or suppositories can help relieve the pain syndrome during the progression of prostate adenoma. The most readily available of these is metazole sodium. However, this drug can only be used for a single use because it can only work on mild pain syndromes. In addition, analgesics using lidocaine, benzocaine, anesthetics, and Novcaine (extramol, benzocaine, trabenoside + lidocaine) are effective.
Vitamin E 400
Tocopherol acetate or vitamin E are usually used as antioxidants, radioprotectants and irreplaceable links in the reproductive process, and are widely used in the comprehensive treatment of prostate adenomas. The urologist's vitamin E dosage is 400 mg, which is suitable for patients with erectile dysfunction and spermatogenesis related to prostate adenoma.
Urologists should prescribe and supervise the treatment of serious chronic diseases such as prostate adenoma. It is strictly forbidden to take certain medications without first consulting a doctor, because self-medication in this case may not only be ineffective, but also dangerous to men’s health. Only qualified experts can tell you which prostate adenoma drugs are the most effective in each case and which ones can cause negative consequences.

Mode of operation
The hospital's urologists skillfully perform classic and minimally invasive surgical interventions, using innovative surgical treatment methods for prostate adenoma. Choose the most suitable surgery for each patient.
The accepted standard in the surgical treatment of prostate adenoma is transurethral resection of the prostate. The operation efficiency is very high. After the intervention, the patient got rid of bladder outlet obstruction (narrowing of the urethra) and related symptoms. The recovery period is short. During or after the operation, bleeding may occur, which is a syndrome of "water intoxication" in the human body.
Other methods of treating prostate adenoma include the following surgical procedures:
- Bracket
- Balloon expansion;
- Hyperthermia;
- Hyperthermia;
- Ultrasound, laser and needle ablation;
- Interstitial coagulation.
After them, the frequency of complications has decreased, but these techniques are not as effective as transurethral resection in terms of clinical and economic terms.
When the tumor grows significantly, a laparoscope can be used to remove the prostate adenoma, and transurethral resection can be problematic. This operation is difficult and needs to be performed under general anesthesia. Through a small incision, the surgeon introduces a special instrument into the body cavity and uses it to remove prostate adenomas. The operation is performed based on the image from the camera, which is displayed on the screen. The main advantages of the intervention are minimal blood loss and low complication rate. After the operation, the patient does not need long-term recovery.
When men show signs of prostate adenoma, doctors will use high-tech methods to treat the adenoma-laser enucleation. The intervention is for large tumors. Use laser to remove excess tissue. The operation is performed through the urethra. The tumor is separated, divided into small parts, and then excreted. This method is considered minimally invasive. It has many important advantages: it will not destroy the integrity of the cavity and will not cause unnecessary damage.
Laser vaporization is the destruction of adenomas by laser vaporization. The urologist introduces a special device through the urethra, takes it to the tumor, and directs it with a strong green laser. The penetration depth of the laser and the accuracy of its hitting can avoid damaging adjacent areas. The method is minimally invasive, bloodless, fast and effective. Its only disadvantage is that the tumor tissue cannot be used for histological examination.
In some cases, the inevitable method of treating prostate adenoma is abdominal surgery-adenoma resection. Perform this operation when other methods cannot help the patient. During the operation, the surgeon uses a scalpel to enter the prostate and uses surgical instruments to manually remove the adenoma. The results of the surgery may cause massive blood loss and may cause complications. After the operation, the patient needs long-term recovery.
Removal of prostate adenoma by transvesical (transvesical) gland resection involves radically removing hyperplastic prostate tissue through a longitudinal incision in the anterior abdominal wall and bladder. Surgery is performed in the late stage of the disease. When the tumor reaches a large size, urine accumulates due to the overflow of the bladder, which causes the bladder to overstretch and progress to kidney failure.
The bladder has been pre-inserted with a catheter and filled with a sterile solution of nitrofurazone or other substances. It is then isolated and placed on two special brackets to lift the organ wall. The surgeon dissected the formed folds and opened the bladder.
Along the inner end of the installed urinary catheter, it determines the area around the bladder neck and urethral opening that appears in the visual field, 0. 5 to 1 cm away from it, so that an incision membrane is made in the mucosa. After that, the surgical urologist used his finger to penetrate the thickness of the prostate, allowing it to enter between the tumor capsule and the adenoma node, and excrete the latter. At the same time, the doctor uses the fingers of the other hand (previously inserted into the patient's rectum) to send the glands into the front wall of the abdominal cavity. It becomes easier to operate. Due to the use of this technology, it is possible to shorten the operation time and reduce blood loss.
The surgeon then stops the bleeding (stop bleeding) of the removed adenoma bed and sutures the bladder, leaving a small drainage on the wound. It is designed to flush out blood clots that have formed. The catheter inserted before the operation was not pulled out within 7-10 days. A new part of the urethra is formed around it, rather than the prostatic part of the urethra that is removed during surgery.
Transcatheter adenectomy is one of the most invasive techniques of all techniques used for prostate adenoma. It is accompanied by the risk of the following complications:
- Bleeding from the tumor bed;
- Congestive pneumonia;
- Constipation is manifested by the destruction of intestinal motility evacuation.
In order to avoid complications, the patient should be activated as soon as possible after the operation in the hospital. Surgical removal of prostate adenoma may have the following undesirable consequences:
- Inadequate bladder drainage;
- Narrow his neck;
- Urine infiltration of tissues around the bladder;
- Formation of "front bladder" (residual cavity at the resection of prostate adenoma);
- The formation of narrowing of the lumen of the urethra;
- Urinary incontinence.
This adversely affects the patient’s quality of life and prolongs the urination time so that you can urinate adequately.
When a laparoscope is used for intervention, the consequences of the operation are not obvious. Laparoscopic prostate adenoma surgery is one of the less invasive options for surgery on the prostate. If the patient has a large enough prostate adenoma, the hospital urologist will use this technique.
If the size of the prostate in a patient with adenoma does not exceed 120 cm3, transurethral resection of the prostate adenoma is recommended. But for 10% of patients who require surgery, this option is not appropriate because the size of the gland exceeds 120 cm3. Laparoscopic surgery is not performed to remove urinary tract stones, inguinal hernias, bladder diverticula, and prostate adenomas with ankylosis of the lower extremities. In this case, the urologist, andrologist, abdominal surgeon, and other hospital experts jointly determine the possibility of surgery.